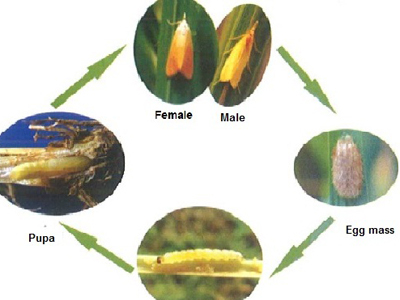
Symptoms
- All stages of the crop are infested by the insect.The caterpillar grows by feeding on the internal tissues of the stem. In the vegetative phase the central shoot dries off turning yellow in colour causing “dead heart”.
- In the ear bearing stage the ear-head appears completely chaffy and white in colour causing “white ear head” .
- Both dead heart and white ear head come out easily while pulled up.
- Generally high borer infestation is seen in rice during October- January and low infestation in crops planted from June to October.
- The infestation is negatively correlated with rain fall and minimum temperature and positively with maximum temperature.
Procedure for Observation
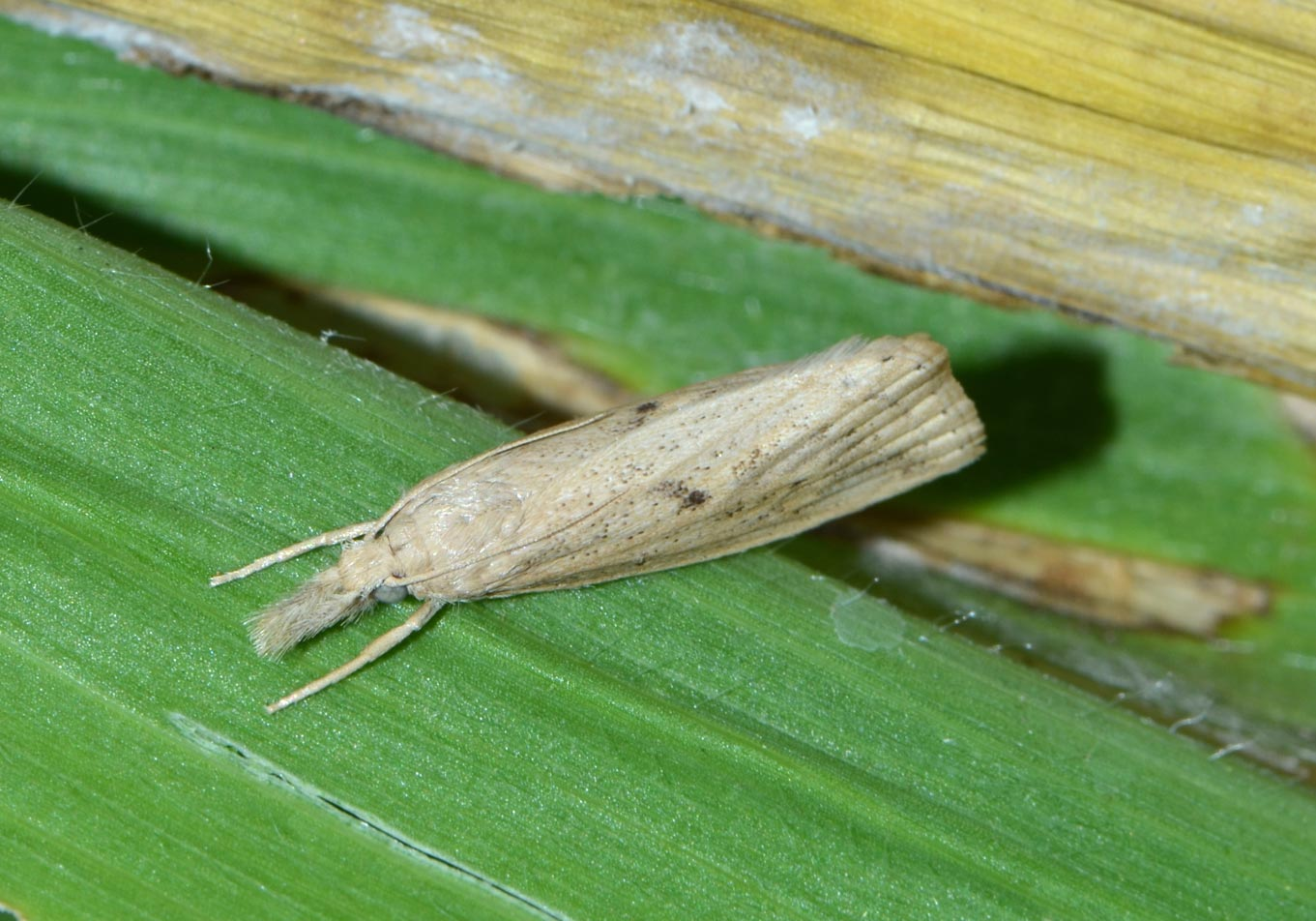
Randomly mark 4 sq.meter plots in 0.4 Ha .Record the total number of stem borer egg masses/moth per sq. meter and percentage of dead heart/white heads and work out the average.