Symptoms
- With the appearance of new flushes beetle lays eggs on them. Emerging grubs bores in to tender shoots and as a result the tender shoots dry. Beetle also lays eggs on tender leaves, the emerging grubs scrape and feed on leaves.
- Portions of leaves subjected to attack by the grub later dries and are blown away by wind and result in the formation of holes on leaves.
- Beetle also feeds on leaves resulting in feeding holes.When spikes are formed the beetle lays eggs on the spike.
- The emerging grubs bore in to the spike and the spike beyond the area of damage breaks resulting in "murithiri"(broken spike). When the spike develops and become hard the grub feed on the skin of the spike.
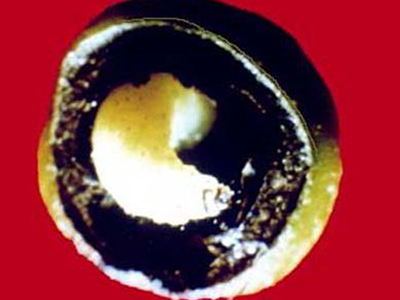
- Damage to spike affects the berry formation badly. When the berries are formed the beetle makes small holes on the berries and lays egg.
- Attacked berries become hollow and crumble when pressed. Such hollow berries are called pollu berries .
Procedure for Observation
Observe 20 standards selected randomly from the plot and assess the % of spikes showing the damaging symptoms by selecting 10 spikes at random from each standard and work out the average. Rate the damage as < 2 % Mild; 2- 4% moderate and >4 % severe.